首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Lasers can cut many types of thin metals, including sheet metal and foil, into complex shapes with high precision. Combining a focused, high-energy laser spot with coaxial gas assist enables clean cuts that require no further processing.
Lasers can cut many types of thin metals, including sheet metal and foil, into complex shapes with high precision. Combining a focused, high-energy laser spot with coaxial gas assist enables clean cuts that require no further processing.
Many industries use lasers to cut thin metals, such as automotive, appliance, electronics, energy, and medical device manufacturing. Benefits include:
Non-contact cutting, lasers do not require sharpening and replacement of cutting blades. They also eliminate the extra force applied to thin metals - preventing warping and other damage.
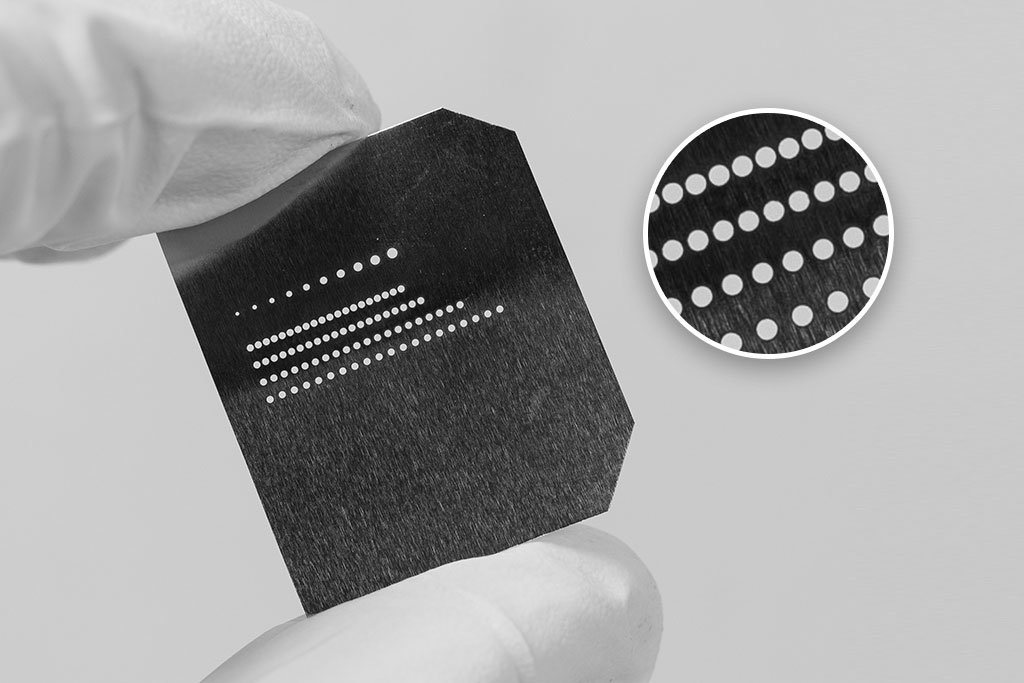
Precise control. Focused, localized laser energy enables very narrow cuts with small kerf widths:. Lasers can also cut fine, intricate patterns into sheet metal and thin foils.
No consumables. Unlike other methods, lasers do not require additional consumables. For example, plasma cutting requires a specific gas mixture to cut metal, while water jet cutting uses a mixture of water and abrasives that must be replenished and properly disposed of. Gas-assisted laser cutting, on the other hand, uses only dry air or standard inert gases.
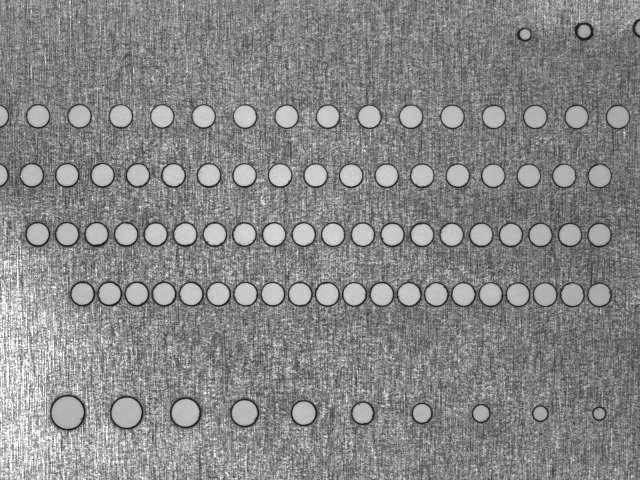
Laser wavelengths used for thin metal cutting applications range from UV to NIR. High-speed fiber lasers (1064nm) can quickly melt and ablate metals, while diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) lasers are suitable for applications that require higher precision.
In addition, UV lasers can achieve precise and detailed cutting with minimal kerf width and low heat-affected zone. If your application requires a clean cut edge, you can also use a UV laser. Finally, ultrafast femtosecond and picosecond lasers achieve the best cut quality and can be used to cut both metals and coated metals.
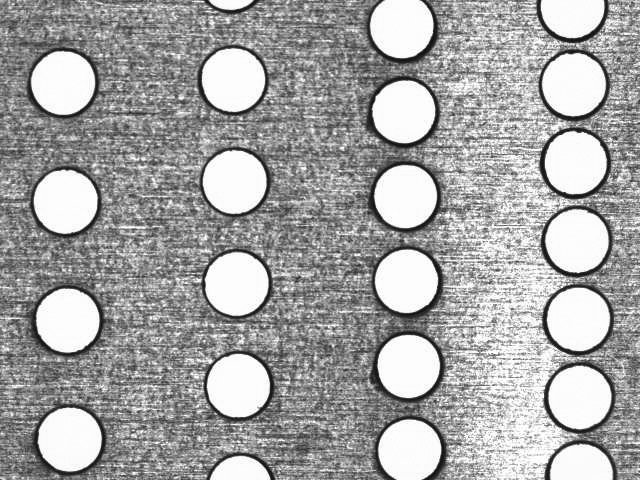
The two most common laser cutting methods are:
Gas-assisted thin metal cutting: A gantry or motion table moves the laser head and the metal sheet - achieving a complete cut in one pass: depth. Coaxial gas assist further reduces the cutting head impact zone and oxidation while preventing slag on the back side.
Galvanometer-controlled thin metal cutting: Using galvanometers to control the beam is another way to laser cut thin metals. Computer-controlled galvanometers enable high-speed cutting patterns, as well as rapid multiple passes of the same pattern, reducing thermally induced strains on the part.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What are the laser equipment i