首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Thermoplastics can be divided into amorphous and semi-crystalline thermoplastics. Amorphous thermoplastics are transparent because they have no visible additives. On the other hand, semi-crystalline thermoplastics appear opaque or milky to the naked eye. In principle, identical thermoplastics can be welded together with a laser. However, the optical properties of the thermoplastics must be taken into account.
Thermoplastics are plastics that can be melted. They are therefore weldable. The two types of thermoplastics and the principles of weldability of the two materials are explained in more detail below.
Thermoplastics can be divided into amorphous and semi-crystalline thermoplastics. Amorphous thermoplastics are transparent because they have no visible additives. On the other hand, semi-crystalline thermoplastics appear opaque or milky to the naked eye. In principle, identical thermoplastics can be welded together using a laser. However, the optical properties of the thermoplastics must be taken into account.
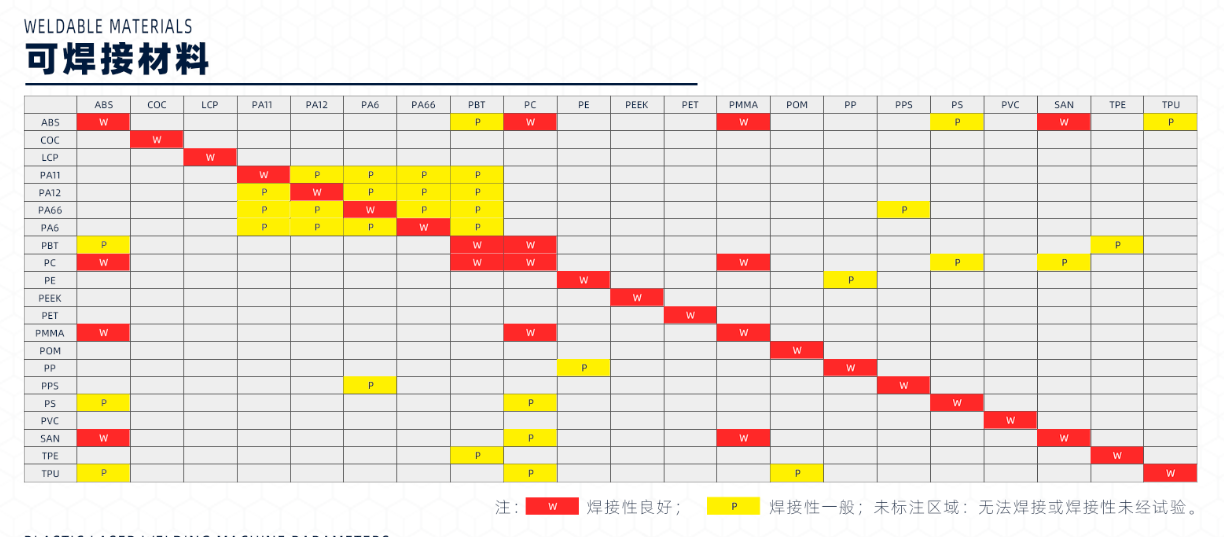
The table lists the material combinations that can be laser welded. In addition to these combinations, modified mixtures can also be used to expand the spectrum.
Full-size image Material combinations:
Optical properties
The optical properties of plastics influence the welding results in laser welding. On the one hand, laser welding requires a transparent welding partner.
Without additives, every thermoplastic is transparent for laser radiation. However, a distinction is made between amorphous and semi-crystalline thermoplastics. With amorphous thermoplastics, the radiation is transmitted almost perfectly even with thicker materials. With semi-crystalline thermoplastics, on the other hand, the radiation is refracted and reflected at the crystallites. This results in a scattering of the radiation, which depends primarily on the degree of crystallites and the thickness of the material to be irradiated.
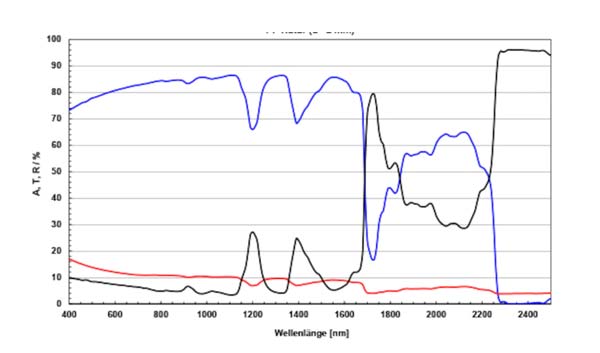
The figure below shows the spectrum analysis of transparent polypropylene (PP). Plastics are more transparent in the wavelength range of 800-1100 nm than in the visible light range (400 - 700 nm).
Optical penetration depth
Optical penetration depth is a measure of the properties of the absorptive joining partner. It shows how deeply the radiation penetrates the plastic surface before generating heat.
Ideally, the optical penetration depth is in the 渭m range, see the figure above. If there is not enough absorption, volumetric absorption is more likely to occur. This heats up the entire thickness of the material, see the middle case. The third case describes too great a surface reflection. In this case, the radiation cannot penetrate the surface at all. The last two cases are therefore quite unfavorable for the process.
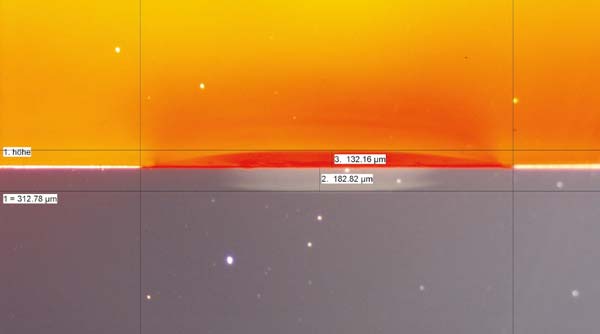
The heat generated during welding forms a heat-affected zone that can be seen under a microscope by microtome sections or microtomes.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: Carbon dioxide paper laser cut