首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
During the laser welding process, the fusion area presents a teardrop shape, which is mainly composed of a circular cavity at the top, a molten area in the middle, and a small cavity at the bottom. Among these defects, the top and bottom holes are prone to stress concentration, and poor parameter control can easily cause cracks. In addition, due to the existence of the droplet structure, poor line spacing control can cause intermittent non-welding.
Having worked in the laser industry for many years, Laisai is mainly engaged in the application of laser cutting equipment and laser welding equipment. Now, let's take a look at what kind of sparks will be produced when the glass industry is combined with laser welding technology.
With the rapid development of 5G, wireless charging, optical communication and chip technology, glass materials have low electromagnetic signal shielding rate, high hardness, light weight and low cost. It is suitable for mass production and has gradually become the mainstream material for 3C electronic structural parts (such as mobile phone glass shells), semiconductor devices (crystal components and panels), optical components and camera modules; the FRP welding processing industry will have a good prospect.
Different types of glass, glass and single crystal silicon welding have been realized one after another. Laisai uses a special laser single-line/multi-line scanning method to achieve glass welding and sealing. On the microstructured optical fiber, laser micro-arc welding was used to form a 100-micron-thick micro-arc weld to form a standard optical fiber welding end cap for optical fiber and microstructure. Tamaki et al. successfully welded different glasses, glass and silicon wafers using a laser with a wavelength of 1558nm, and obtained welding strengths of 9.87MPa and 3.74MPa.
During the laser welding process, the fusion area appears droplet-shaped, mainly composed of a circular cavity at the top, a molten area in the middle and a small cavity at the bottom. Among these defects, the top and bottom holes are prone to stress concentration, poor parameter control, and easy cracks. In addition, due to the existence of the droplet structure, poor line spacing control will cause intermittent non-welding.
The material used in the experiment is optical glass, the sample size is 25脳25脳1 mm, and the sample size is:
(a) Clean the glass surface. Soak the glass surface for 5~10 minutes, then rinse with distilled water 3~5 times, and finally blow dry the stains on the glass surface with hot air;
(b) Press weld the glass. Put the laminated glass sheet into the fixture positioning groove, adjust the welding fixture mechanism to press down the surrounding area of the glass sheet to make the glass sheet tight. Previous researchers鈥?experimental studies have shown that the bonding gap for glass welding should be less than 100nm (some believe it should be less than one-quarter of the laser wavelength).
(c) Adjust the focus to the joining point of the two pieces of glass. When the laser is transmitted from the air to the glass, refraction will occur and the focus will shift. Therefore, use the glass block attached to find the focus, adjust the height of the vibrating lens perpendicular to the glass surface at equal intervals, scan the glass with the same energy frame, take out the glass piece, and observe the position of the interface where the glass absorbs the laser, that is, the focusing position.
(d) Laser glass welding. Continuously perform steps (b) and (c), press the glass sheets together, adjust the focus to the glass interface, and adjust the appropriate laser welding process parameters (power, speed, scanning pattern, etc.). Welding glass.
At the glass interface, when the high-energy laser exceeds a certain threshold, it will cause multi-photon ionization of the glass material. Ionized free electrons accelerate the collision with other atoms, causing avalanche ionization, increasing the temperature of the material and making the glass reach the melting point.
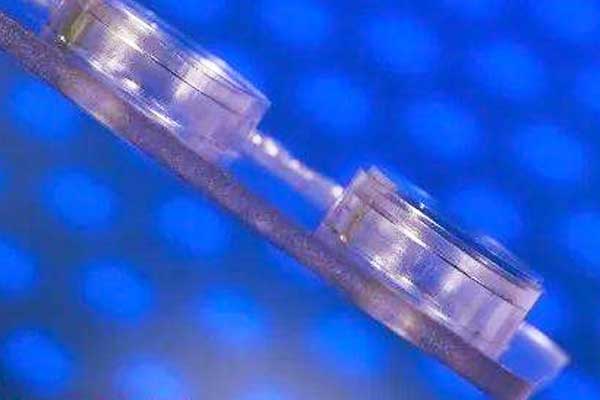
Use special laser welding, full welding area (4脳4mm), uniform welding and forming. After welding, the material has little deformation and little change in flatness. The fusion zone is located at the interface of the two materials, its thickness is small, and the glass in this area has no thermal damage.
The end-face slice of the glass after welding shows that under the new laser welding process, there is no teardrop-shaped weld fusion zone, no welding crack source defects in the top circular cavity and the bottom linear small cavity, and no intermittent linear crack defects in the melting zone. When the welding strength test was carried out, the base material broke, the weld did not fall off, and the weld strength was high. Using a special laser light source and adjusting the appropriate welding process parameters, the glass material was nonlinearly absorbed, melted and solidified, so that the two pieces of transparent glass formed a firm welding area, and successfully achieved direct welding between optical glasses. After the two layers of material were fused, the optical glass was welded and fused, without obvious macro and micro cracks, no teardrops, no top teardrop circular cavity and bottom line damage area, and the interface was wireless and unfused, effectively avoiding the crack source. After the strength test, the weld remained on the surface of the specimen, which improved the connection strength.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What role does laser cutting m