首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Lasertech uses innovations in laser technology to develop efficient machine solutions for the production of electronics. The use of ultrashort pulse lasers ensures optimal processing results when drilling, scribing, cutting and structuring circuit board materials, ceramic substrates and semiconductor wafers. Galvanometer scanners or fixed optical processing heads can be combined in each machine. One machine can also cover two-stage processes. PCB Laser Processing Laser Drilling Microvias Laser drilling of blind and through-holes in rigid and flexible circuit boards. Microvias with high aspect ratios and diameters
Laser Laser uses innovations in laser technology to develop efficient machine solutions for the production of electronics. The use of ultrashort pulse lasers ensures optimal processing results when drilling, scribing, cutting and structuring circuit board materials, ceramic substrates and semiconductor wafers.
A galvanometer scanner or a fixed optical processing head can be combined in each machine. One machine can also cover a two-stage process.
PCB laser processing
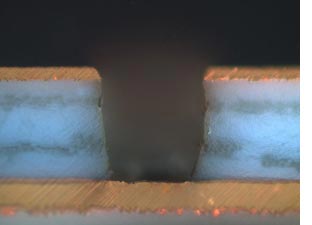
Laser drilling of blind and through vias in rigid and flexible circuit boards. Microvias with high aspect ratios and diameters of <20 渭m. Trepanning or percussion drilling with ultrashort pulse lasers enables an ideal process for a wide range of circuit board materials.
Typical applications: RCC, FR4, FR5, polyimide
Laser cuts outlines (routing) in rigid/flexible circuit boards and cover foils. Clean and high-precision cuts with minimal cutting widths in a variety of circuit board materials.
Typical applications: RCC, FR4, PTFE, CEM, polyimide
Laser Depaneling
Laser cutting of assembled and unassembled circuit boards. Clean and high-precision cuts with minimal cutting widths in a variety of circuit board materials.
Typical applications: FR4, FR5, polyimide

Creating Cavities in Printed Circuit Boards
By using lasers to remove material in a targeted manner, cavities can be created in the circuit board for inserting microchips. The laser process allows precise control of the removal depth and the geometry of the cavity.
Using a suitable laser source and processing strategy ensures high surface quality with minimal thermal stress on the material.
Depending on the application requirements and the selected laser source, the substrate can be processed using either fixed optics or a galvo scanner. Ultrashort pulse lasers produce burr-free score lines and reduce thermally induced material stresses through an almost cold removal process.
Typical materials: AlOx, AlN, DCB substrates, composite ceramics

Laser Cutting Ceramic
Laser cutting creates any geometry with minimal radius in ceramic substrates (internal and external contours). Depending on the application requirements and the selected laser source, the substrate can be processed with fixed optics or galvo scanners. Ultrashort pulse lasers produce burr-free score lines and reduce thermally induced material stresses through an almost cold removal process.
Typical materials: AlOx, AlN, LTCC, HTCC, DCB substrates, composite ceramics

Laser Drilling of Ceramics
Laser drilling of ceramic substrates allows for the smallest possible hole diameters (<40 渭m). Depending on the hole diameter, trephine or percussion drilling can produce the ideal hole geometry in AlOx, AlN, LTCC, HTCC, DCB substrates and composite ceramics.
Ultrapulse lasers produce burr-free holes and reduce thermally induced material stresses through an almost cold removal process.
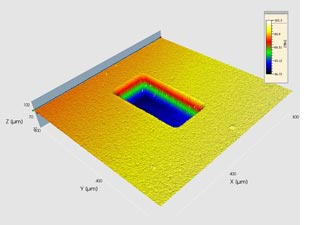
Creating Cavities in Ceramics
By using a laser to remove material in a targeted manner, cavities can be created in ceramic substrates, in which the microchips are inserted. The laser process allows precise control of the removal depth and the geometry of the cavity.
The use of suitable laser sources with pulse lengths in the nanosecond and picosecond range ensures high surface quality with minimal thermal stress on the material.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: How is electronic paper cut du