首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
PCB, which stands for printed circuit board in Chinese, supports and electrically connects electronic components. As a type of PCB, the base material of metal-based PCB is usually made of metal (such as aluminum and copper) with good heat dissipation.
What is a metal-based PCB board:
PCB Chinese name is printed circuit board, which supports and electrically connects electronic components. As a type of PCB, the base material of metal-based PCB board is usually made of metal (such as aluminum, copper) with good heat dissipation. Therefore, no radiator is required, the product volume is reduced, the heat dissipation is excellent, and it has good insulation and mechanical properties.
Aluminum-based PCB board is the most widely used metal substrate at present, and is commonly used in LED lighting products. The aluminum-based PCB boards on the market now are generally single-sided aluminum substrates. Single-sided aluminum-based PCB boards are usually composed of three layers: circuit (copper foil), insulation layer and metal substrate. A circuit (i.e. copper foil) is usually formed into a printed circuit by etching, so that the various parts of the component are connected to each other. Generally speaking, the circuit layer requires a lot of current carrying capacity, so it is necessary to use copper foil with a thickness of generally 30渭~280渭m. Thermal insulation is the core technology of aluminum substrates for printed circuit boards, which is usually composed of polymers filled with special ceramics. It has the characteristics of low thermal resistance, good viscoelasticity, good thermal stability, good aging resistance, and high resistance to mechanical force and thermal stress. The single-sided aluminum-based PCB board has two sides, the white side is used to solder LED pins, and the other side is used to solder aluminum. It is generally coated with thermal conductive slurry and then in contact with the thermal conductive part.

Traditional production process of aluminum-based PCB boards:
When conventional PCB factories produce metal substrates, they generally use CNC gong machines or punching machines for stamping. The processing flow is as follows:
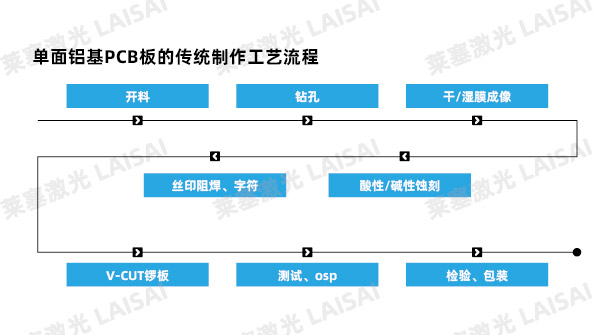
Because it is a contact processing, the wear of the tool during the processing of the gong plate machine is large, and the processing quality is reduced due to wear. The contact head processing also has the disadvantages of low precision, large cutting gap, and deformation of the substrate. Stamping processing first requires the mold to be made, but the mold opening cost is high, the cycle is long, and the board edge is prone to collapse during the processing. In addition, these two processing methods are more suitable for mass production. For small-batch processing, both have the disadvantages of high cost and long cycle.
Application characteristics of fiber-based laser cutting PCB boards:
Based on metal PCB laser cutting, the thickness is usually 1-2 mm. According to the thickness of the material, choose a continuous fiber laser for cutting, or choose a quasi-continuous fiber laser with corresponding power according to the processing requirements and cut in pulse mode.
No matter what kind of fiber laser is used, laser cutting of aluminum-based PCB boards has the following characteristics:
1. Good processing quality: the edge of the cut is smooth and burr-free.
2. High processing efficiency and fast cutting speed.
3. High processing accuracy 鈼?Low processing cost:
1. The laser cut seam is small, the utilization rate of the laser cut plate is high, and the material cost is low.
2. Non-contact processing, no tool wear.
Fourth, high process flexibility: not limited by graphics, PCB boards of any shape can be processed.
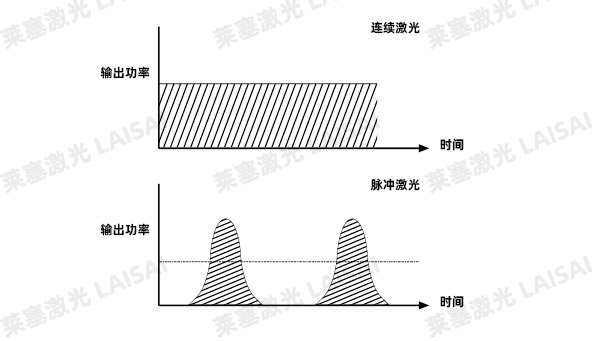
Quasi-continuous fiber laser cutting of aluminum-based PCB boards:
Quasi-continuous fiber lasers can work in continuous high peak power pulse mode at the same time. In continuous mode and modulation mode, the peak power and average power of continuous laser are always the same, while quasi-continuous laser is different. Its peak power in pulse mode is several times the average power, so it can generate high-energy pulses of microsecond and millisecond pulse energy at a repetition frequency of hundreds of hertz to thousands of hertz, thereby achieving excellent processing. Compared with continuous laser cutting, quasi-continuous laser cutting of aluminum-based PCB boards generally adopts pulse output, and the cutting application has the following characteristics:
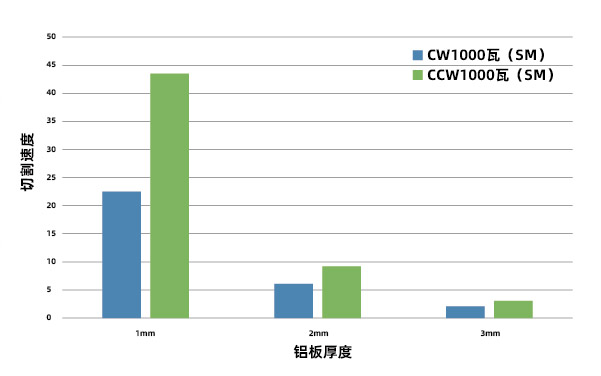
High-speed cutting is mainly because the thickness of aluminum-based PCB boards is generally 1~2mm, and nitrogen-assisted melting cutting process is usually used in laser cutting. During the laser melting cutting process, metal materials absorb laser energy and convert it into heat energy, thereby melting metal materials. According to the theory of thermal equilibrium, fusion cutting has the following empirical formulas:
P=K*(t*v*蠅)
In this value, P represents the laser power absorbed by the material, K is a fixed value determined by the plate, t represents the cutting speed, v represents the cutting speed, and 蠅 represents the cutting width. The results show that when the laser absorption power is constant, the smaller the slit width 蠅, the faster the cutting speed. When using a high beam quality laser to cut thin plates, the slit width 蠅 can be made very narrow, and more effective cutting can be obtained by absorbing the same laser energy. The quasi-continuous fiber laser of the Leiser laser has a large peak power, which makes it easier to remove the oxide layer on the surface of the aluminum plate, thereby increasing the absorption ratio of the aluminum plate to the laser; and the output beam is a quasi-fundamental mode, and the fiber core diameter is small, so the slit is narrow and the cutting speed is faster.
The main material of the small insulating layer in the ablation area of the insulation layer is organic resin, which has a low melting point and is sensitive to heat. Quasi-continuous laser cutting uses pulse output, with small cutting heat shadow and small ablation area of the insulation layer.
The small thermal deformation on the automatic mounting line is small. If the circuit board is not flat, it will cause incorrect positioning, and the components cannot be inserted or pasted into the board holes and surface mounting pads, and even damage the automatic mounting machine. The circuit board is prone to bending after welding, which makes it difficult to cut the component feet flat and flat. The IPC standard specifically stipulates that the maximum deformation allowed for PCB boards of surface mounted devices is 0.75%, and the deformation of surface mounted PCB boards is not allowed to be 1.5%. In practical applications, in order to meet the needs of high-precision and high-speed mounting, some electronic assembly manufacturers have strict requirements on the deformation amount, and some customers even require 0.3%. Quasi-continuous laser cutting has little thermal impact on the plate, so the thermal deformation of the plate after cutting is small, which is more in line with the strict requirements of aluminum-based PCB manufacturers.
Compared with continuous lasers with the same average power, the edge quality of the cut seam is better. Quasi-continuous lasers have higher peak power, and the cross-section of the cut aluminum sheet is smoother and the micro-burrs are smaller.
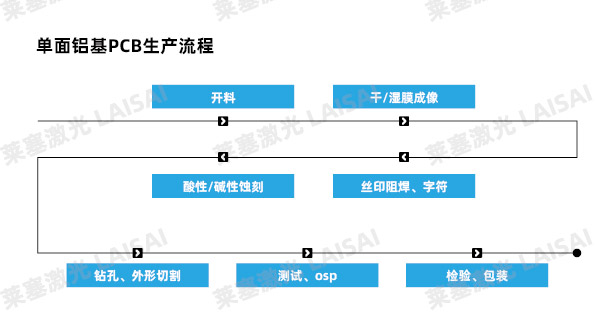
Optimize laser cutting of single-sided aluminum substrates:
In the production of printed circuit boards, lasers can not only cut aluminum substrates, but also drill holes on them. By utilizing the precise focus of the laser beam, not only is the quality of the drilled hole higher, but the minimum diameter of the hole is also smaller than that of mechanical drilling. Therefore, after the introduction of the laser cutting process, the production process of single-sided aluminum-based PCB boards can complete drilling and shape cutting at one time, reducing the number of processes and optimizing the production process.
The development direction of metal-based PCB board cutting technology:
Due to the gradual increase in the prices of domestic raw materials such as copper and aluminum, coupled with the continuous increase in factory rent and labor costs, the profit margins of PCB factories using traditional processing methods are constantly eroded and the pressure they face is also increasing. In order to obtain greater profit margins in the competition, innovative automated processing technology and alternative new processes will become issues that circuit board factories urgently need to solve. Compared with the traditional metal substrate cutting method, laser cutting has the advantages of high quality, high efficiency, high precision, low cost, and high flexibility, and will become the development direction of metal substrate cutting technology in the future. Compared with the same power continuous fiber laser, the quasi-continuous fiber laser has better cutting quality for aluminum-based PCB boards, faster cutting speed, smaller insulation layer ablation range, and smaller thermal deformation of the board. Therefore, it will be more common to use high-power quasi-continuous fiber lasers to cut metal-based PCB boards in the future.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What is the price of UV laser