首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Laser cutting machines are used to process organic glass (acrylic) with high speed, high precision and accurate positioning. They can be used to make craft gifts, panel mirror boxes, model toys, advertising light boxes, signboard displays, packaging boxes, etc.
Laser cutting machine is used to process organic glass (acrylic), with fast speed, high precision and accurate positioning. It can be used to make craft gifts, panel mirror boxes, model toys, advertising light boxes, signboards, display items, packaging boxes, etc.
鈶燝ood cutting effect: no need to throw with fire, very smooth, bright, no sawtooth pattern, can cut 20mm acrylic at one time.
鈶xcellent performance of the whole machine: can work continuously for 24 hours, Taiwan original track, accurate and durable.
鈶ast cutting: such as used to cut 3mm thick acrylic board.
For the past 30 years, laser cutting and welding of thin metal sheets has been done by locally heating the beam. This method is flexible and economical and is widely used in many industrial fields. In fact, the thermal conductivity of glass is lower than that of metal, so it is logical that lasers should be applied to glass cutting. In fact, some companies have been developing complete systems since the 1970s, when kilowatt-class CO2 lasers were used. However, due to the high power, the thermal impact on the glass could not be ignored, and the local material melted. At that time, it was difficult for laser cutting technology to ensure a neat and smooth cutting edge, and in many applications, the cutting edge still needed to be ground. At the same time, CO2 lasers were very expensive at that time.
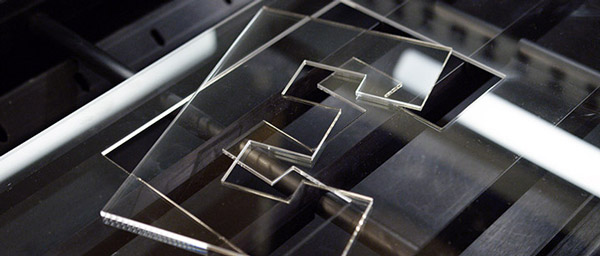
Laser induced separation
Recently, some engineers and scholars have found that low-energy lasers can be used to separate glass without producing thermal effects such as melting. The method is complex in language and involves many detailed technologies. Its basic principle is to use laser-induced stress to "separate" the glass. During this period, with the maturity and development of closed CO2 laser technology, laser cutting glass technology has become more economical and practical.
This study uses a CO2 laser (K-150 model from Coherent) with an average output power of 150W. An elliptical focal point is formed on the glass surface by focusing the optical path to ensure that the laser energy is evenly distributed on both sides of the cutting line. After the glass absorbs the 10.6-micron laser, almost all of the energy is absorbed by the 15-micron absorption layer on the glass surface, compared with the cutting line formed on the glass surface by the laser. Select an appropriate movement speed to ensure that there is enough laser heat to form a local stress distribution (set cutting line) on the glass surface to prevent the glass from melting.
During the laser cutting process, the quenching gas (water) nozzle is the quenching gas (water) nozzle. As the laser point moves, the quenching gas (water) nozzle blows cold air (water) to the glass surface, breaking the cold air (water) with its maximum direction, thereby separating the glass along the set direction.
It should be pointed out that in order to cause the glass to break, a tiny initial crack must first be mechanically scratched at the starting point of the cutting line.
By selecting processing parameters such as laser power and light spot scanning speed, the stress-induced fracture depth can reach 100 microns to several millimeters, that is, the laser method can gradually cut 100 microns to several millimeters of glass.
Since this process depends on thermodynamic stress, its fracture depth and cutting speed are closely related to the expansion coefficient of the material itself. Generally speaking, the expansion coefficient of glass suitable for laser cutting should be at least 3.2x10-6K-1. Fortunately, most ordinary glass can meet this requirement.
Results and applications
This new method has some significant advantages over traditional mechanical cutting methods. First, this process can be completed in one step and dry processing. The edges are smooth and neat, and no subsequent cleaning and polishing are required. Moreover, the laser-induced separation process produces high-strength, naturally tempered edges without micro-cracks. The use of this method avoids unpredictable cracks and residual cracks, reduces the defective rate, and increases production.
Edge Quality
The dynamic differences of three different cuts on a 1.5 mm thick glass sheet were qualitatively analyzed. The cut edge is clean, without cracks, cracks, and no subsequent processing procedures. Since the laser is a contactless tool, there is no tool wear problem, so continuous and uniform cutting thickness and edge quality can be guaranteed. In comparison, 3(b) shows the situation of cutting the edge with a metal wheel, and various residual tension components can be seen along the cutting line. 3(c) is the result of cutting with a diamond wheel. In many applications, many tiny cracks can be seen, and the cut edge needs to be polished.
To quantitatively evaluate the edge quality, the laser cut edge should be measured using a Stylus profilometer in accordance with the requirements of ISO3274. Official tests show that the average roughness (Ra) is less than 0.5 microns.
Border Strength
Due to the good edge quality and the natural tempering effect during the heating/quenching process, the laser cut edge strength is very high. The Otto-Schott-Insititut in Jena has independently tested the DIN5230011 parameters and the relevant data has been published. Using this method, the edge strength was increased by about 30% compared to the machined specimens.
Thickness and Cutting Speed
There are three factors that affect the cutting speed: glass thickness, material thermal expansion coefficient (see Figure 2), and laser output power. This experiment uses a CO2 laser with an output power of 150W, cutting a=7.2x10-6, glass thickness of 1.1mm, straight cutting, and a speed of 500mm/s. In contrast, the same thickness of glass can be cut with the same hard metal wheel at a speed of up to 1500mm/s. However, even in applications where speed is important, the economic and quality advantages brought by laser cutting can make up for this difference. We all believe that further optimization of the processing technology and the use of laser cutting with a larger output power can increase the processing speed by 2-3 times.
Curved Cutting
Since the crack is a precise mark on the laser beam, laser-induced separation can cut very precise curved patterns. In fact, the experiments we have conducted have also proved that laser cutting can achieve continuous and accurately set patterns in straight or curved situations with a repeatability of up to +50渭m. This allows accurate cutting of curves and three-dimensional graphics.
application.
Laser separation technology will replace mechanical methods in many glass cutting applications. In recent years, laser cutting has shown strong technical advantages in the following three application areas: CRTS, flat panel displays, automotive windshield cutting, etc.
Some applications require special post-treatment of the glass, for example, certain safety glass components need to be temperature hardened, and most silicon-coated flat panel display components must undergo temperature annealing, etc. This special post-treatment method is matched with the laser-induced separation method. We cut 100 pieces of 4 mm thick glass without damage during the special heat treatment process.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: Application of laser cutting m