首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Plastic is a polymer commonly known as plastic or resin. It is made from monomers through addition polymerization or condensation polymerization. The components and shapes can be changed at will. It is composed of synthetic resins and additives such as fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, lubricants , and colorants.
Plastic is a polymer often called plastic or resin. It is obtained by addition polymerization or condensation polymerization with monomer as raw material. The components and shapes can be changed at will. It is composed of synthetic resin and additives such as fillers, plasticizers, stabilizers, lubricants, and colorants.
Plastic can be divided into two categories: thermosetting and thermoplastic. The former cannot be reshaped and used, while the latter can be repeatedly produced. Its physical elongation is relatively high, generally 50%~500%. At each elongation, the force does not change completely linearly.
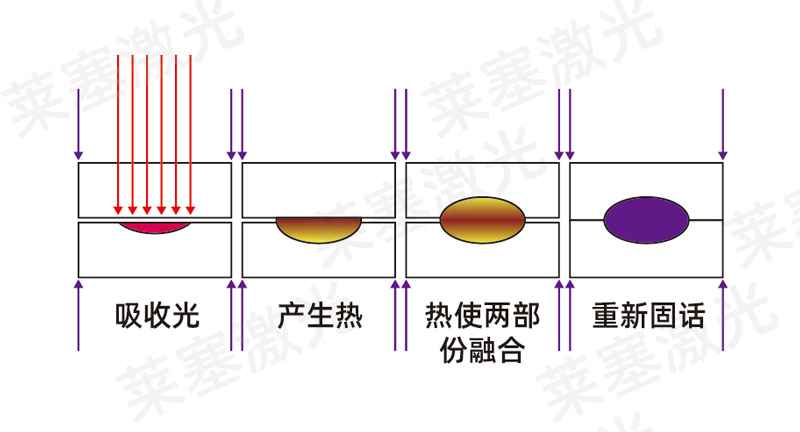
Plastic welding principle
A laser transmission welding method: its premise is that one of the two parts can transmit light, and the other part must be able to absorb laser. During welding, the laser beam passes through one part and is then absorbed by the other part at the contact surface between the two parts. During the welding process, the laser beam is absorbed by the other part to form a heat action zone; during the welding process, the laser beam passes through one part and then diffuses mutually on the contact surface of the two parts, thereby forming a tightly connected material, and the parts to be welded are connected.
Therefore, one side of the welded plastic is a transmissive material that passes the laser, and the other side is an absorptive material that absorbs the laser. An absorbent (carbon black) is often added to improve the absorptiveness of the absorptive material. In addition, in order to improve the laser transmission performance through the material, a high-transmittance dye is usually added.
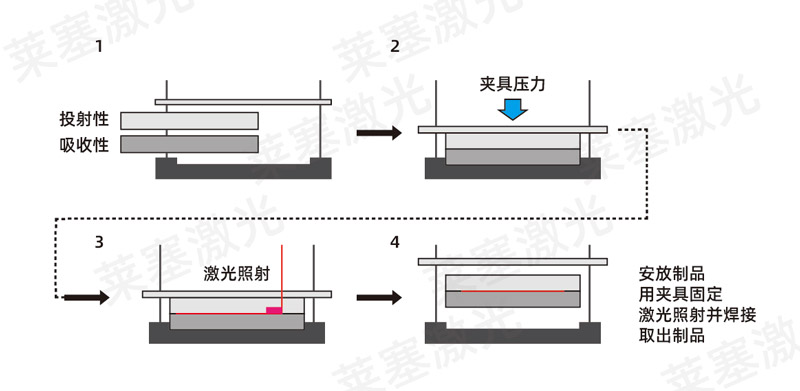
Laser Welding Characteristics
Benefits:
1. Not affected by physical factors such as vibration or ultrasound, suitable for precision parts;
2. Non-contact welding, no thermal effect, scratches or deformation on the surface;
3. Clean working method without dust, flash and other undesirable phenomena;
Higher bonding strength and sealing can be obtained by using the best process conditions;
5. The influence caused by heat can be minimized by narrowing the beam;
6. The resin degradation is small, the generated debris is small, and the surface of the product can be tightly bonded around the weld.
Disadvantages:
1. There are restrictions on existing materials (must be used in combination with penetration and absorption materials);
2. The overlap welding of two transparent materials requires the addition of absorbent (currently only imported products, the price is very expensive);
Current welding methods:
1) Outline welding
The principle of outline welding is as shown in the figure: the laser spot moves in sequence according to the predetermined two-dimensional or three-dimensional linear trajectory to complete the welding action. Of course, the spot can also be fixed and the workpiece moves in a straight line to complete the welding. The principle is the same, and both have relative motion. Shape welding has high flexibility. The laser welding head equipped with a multi-degree-of-freedom manipulator can easily complete the welding of complex three-dimensional curves. It has high energy utilization and is easy to load. However, due to the single-point linear motion, it is difficult to greatly improve the welding efficiency and is only suitable for small-batch production.
(2) Mask welding
The principle of mask welding is shown in the figure. A layer of mask is placed between the laser light source and the workpiece to be welded. The diaphragm is designed according to the required welding contour. When the contour is transparent, the non-weld point is a non-weld point. Since the welding accuracy reaches the micron level, this welding method has extremely high welding accuracy and high welding efficiency. However, only part of the laser is involved in welding, resulting in low laser power utilization.
3) Synchronous welding
The principle of synchronous welding is shown in the figure. Multiple laser beams are shot to the contact surface of the workpiece, so that the entire welding contour melts at the same time. After cooling and solidification, welding can be carried out. In order to ensure uniform distribution of the weld, it can also be avoided in the same plane. At the same time, the welding speed is fast and the efficiency is high, which is suitable for mass production, but the formed parts are expensive and require daily maintenance.
4) Quasi-synchronous welding
The principle of quasi-synchronous welding is shown in the figure. It is a welding method that combines contour welding and synchronous welding. Quasi-synchronous welding is relative contour welding. Its laser spot moves faster and can heat the entire weld contour at the same time, thereby reducing welding defects. Due to its fast welding speed, quasi-synchronous welding can greatly shorten the welding time, but due to the maximum width of the scanning galvanometer, there are certain requirements for the workpiece size during the welding process. It is suitable for welding small, high-precision parts, such as precision sensors, microelectronics, etc.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: Laser cutting acrylic billboar