首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
How is light produced? 1) Composition of matter Any visible macroscopic matter is composed of particles such as atoms, molecules, and ions. In this case, molecules are atoms bonded together by covalent bonds, and ions are atoms bonded together by ionic bonds.
How is light produced?
1) Composition of matter
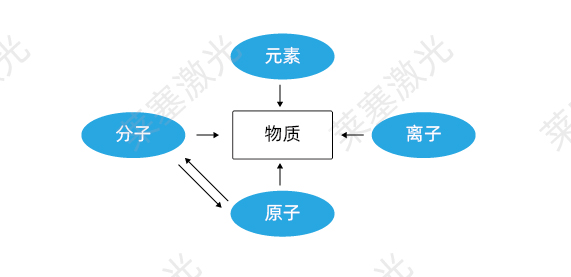
Any visible macroscopic matter is composed of particles such as atoms, molecules, and ions. In this case, molecules are formed by atoms combined through covalent bonds, and ions are formed by atoms combined through ionic bonds, so in the end, matter is composed of atoms, as shown in Figure 1-1.
2) Atomic structure
As shown in Figure 1-2, an atom consists of a positively charged nucleus and extranuclear electrons located at the center of the atom.
According to quantum mechanics, electrons in the same atom move in non-continuous orbits and can be transmitted along different orbits.
Move, just like a car can drive fast on a highway and slow in a city.
As shown in Figure 1-3, in Bohr's atomic model, there are three electron orbits, and the corresponding different orbits have three different energy levels.
If n=1, the distance between the electron and the nucleus is very small, and the atom is in a stable state at a low energy level, also called the ground state*
|>1, the distance between the electron and the nucleus becomes larger, and the atom transitions to a high energy level unstable state, also called an excited state.
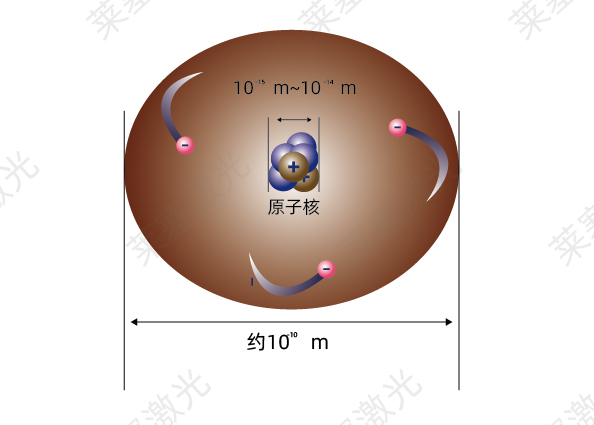
Figure 1-2 Diagram of the structure of atoms Bohr's atomic model
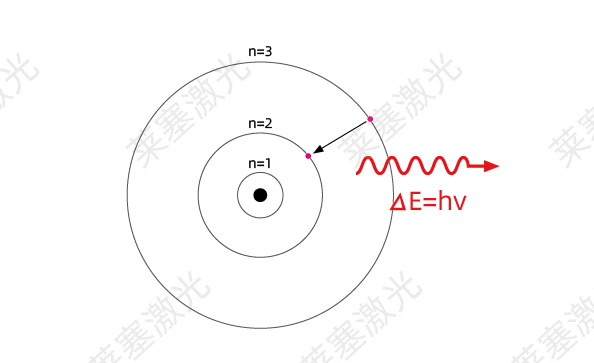
Bohr's atomic model
3) Atomic luminescence
Atoms in an excited state will not stay at a high energy level for a long time, but will spontaneously jump to a low-energy ground state and release excess energy.
If an atom releases energy in the form of photons, this transition is called a spontaneous radiation transition. During this process, the substance will emit light at a specific frequency, and its frequency depends on the energy difference between the two energy levels where the transition occurs:
V=(E2-E1)/h, where 4 is Planck's constant, and 6.626X1034j times s;v represents the frequency of light, lS-1.
Spontaneous transition is a light-emitting method for other sources except lasers. It is a random transition process, and the emitted light is unrelated in phase, polarization state and propagation direction.
From this point, it can be seen that the essence of the emission of matter is that the atoms, molecules or ions of the substance transition from a high energy level to a low energy level in a high energy state, and spontaneously release excess energy, as shown in Figure 1-3.
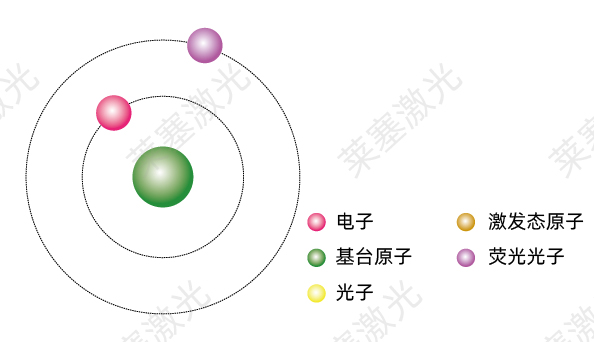
The nature of luminescence of matter
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What are the main metal materi