首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Laser technology is widely used in the manufacturing process of medical devices, including marking, welding, cutting, micro-machining, etc. It is a veritable Swiss Army knife. This article introduces four applications of industrial lasers in medical device manufacturing and the most efficient products.
Laser technology is widely used in the manufacturing process of medical devices, including marking, welding, cutting, micro-machining, etc. It is a veritable Swiss Army Knife. This article introduces four products of industrial laser applications in medical device manufacturing.
1. Laser marking - used for information identification and traceability of enterprises, products and parts
Our common medical devices, including bone screws, pacemakers, hearing implants, endoscopic equipment, etc., will be marked with lasers. Laser marking can permanently provide company and product information, is corrosion-resistant, and ensures long-term traceability. It is a method of directly identifying parts and is also an identification method recognized by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
There are several different lasers for laser marking. These lasers can be divided into ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), far infrared (FIR) and ultrashort pulse (USP) picosecond and femtosecond lasers, depending on the product material.
For stainless steel medical devices, the marking must meet the following conditions:
Corrosion resistant
No surface inclusions
Biocompatibility
Ability to withstand multiple cleanings
For stainless steel, USP lasers meet the above conditions and can pass the rigorous hot nitric acid test to achieve the best overall effect.
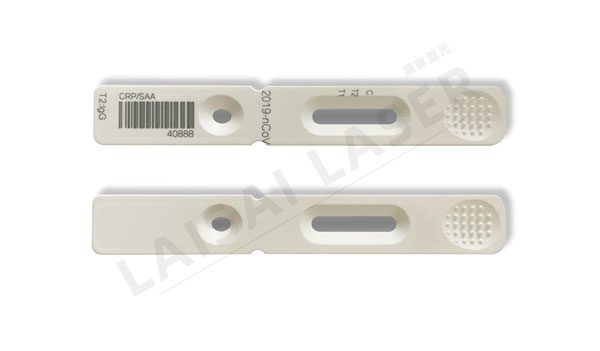
2. Laser welding - an ideal method for connecting very small and complex parts
Applied to spot welding, seam welding and sealing of small precision medical equipment. Parts or local locations with a size of less than 1 mm can be welded. This micro welding is often used in pacemakers, surgical blades, endoscopic instruments and batteries.
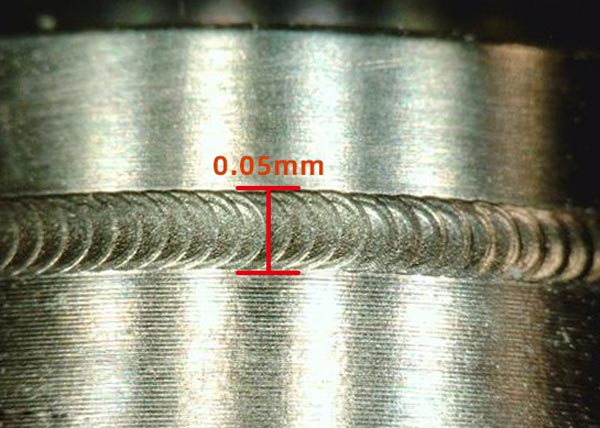
Lasers used for micro welding include pulsed Nd:YAG, continuous wave (CW) fiber, nanosecond fiber, quasi-continuous wave (QCW) fiber, and high-power amplifier (HBDD) laser. Care should be taken to select the most suitable laser according to different applications.
Lasers can be used for spot welding. 20-200 micron spot 鈫?fiber laser; 200-1000 micron spot 鈫?pulse laser.
Pulsed nanosecond laser (Ns) is the best choice for welding very small metal parts, with a metal part thickness of only 0.25 mm and a spot size of less than 50 microns. Pulsed Ns laser is suitable for welding almost any material, providing new opportunities for the combination of small parts and new materials.
In addition to metal welding, lasers are also widely used in plastic parts welding, which is clean, pollution-free and beautiful.
Third, laser cutting - blades, shafts, sleeves, etc., can be precisely cut
Laser cutting technology is very suitable for cutting razors, precision shafts, brackets, sleeves, hypodermic needles, etc.
Laser cutting is generally divided into two methods:
Gas-assisted cutting is usually used with microsecond lasers. Laser ablation is a method of directly ablating the surface of a material using a nanosecond, picosecond or femtosecond pulsed laser, without any post-processing steps and with minimal heat-affected zone. Gas-assisted cutting is the most commonly used method for laser cutting medical device products, with speed and accuracy sufficient to ensure good cutting quality and cutting width. However, as the diameter and characteristics of pipes become smaller and smaller, the use of laser ablation technology is more effective. This technology can achieve cutting of feature sizes and incision widths of 10 microns.
4. Laser micromachining - precision surface structure and drilling
Laser micromachining is suitable for the manufacture of medical devices, such as surface texturing and drilling of needles, catheters, implantable devices and micro-instruments. Commonly used ultrashort pulse (USP) lasers. Due to the short pulse continuous time, material can be removed more effectively, that is, less energy output, good cutting effect, and almost no post-processing is required.

Laser micromachining processes are not particularly fast, but they are very precise processes. The typical application of femtosecond ultrashort wave pulse lasers in polymer surface treatment can achieve precise control of elevation processing and elevation processing.
Uninterruptible power supply lasers can also drill very small and precise holes in needles, with diameters of only 80-200 microns. In addition, laser micromachining systems can also be programmed to process round holes, square holes or elliptical holes to help control the delivery of drugs through needles. Lasers can also process different types of microstructures in different materials, including metals, polymers, ceramics and glass.
Another major application of laser micromachining is wire lift-off. In this application, a femtosecond laser removes a 20-micron thick layer of polyurethane coating by selective ablation without damaging the underlying material.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What are the processing method