首页 > NEWS > Industry News
【summary】
Lasers are very attractive tools for joining thermoplastics and textiles in sheets, films and molds. They have the property of delivering controlled energy directly to the right part of the desired weld accurately and quickly.
Lasers are very attractive tools for joining thermoplastics and textiles in sheets, films and moulds. They have the property of being able to correctly and quickly direct controlled energy to the right part of the desired weld.
Lasers have different wavelengths, which have a great influence on the interaction of light with plastic materials. The nature of the process depends on the type of plastic, thickness and the amount of additives. Complex shapes can be welded with lasers with high positioning resolution and widths less than 100渭m, so they can be processed into various types of products using different material processing equipment, including catheters, microfluidic control devices, pipes, packaging, electronic product boxes, inflatable devices, etc.
鈻燩lastic Types
Thermoplastics are made of long-chain molecular polymers above a certain temperature and can be reprocessed into different shapes or welded. Unlike other thermosetting polymers that cannot be melted, the molecular chains of thermoplastics are not cross-linked and do not have a rigid network. At high temperatures, the molecules can move freely and the material can flow like a liquid. The melting or softening temperature of industrial plastics is between 120-343掳C. Thermoplastics can be divided into semi-crystalline (milk-like appearance) and non-crystalline (vitrified). Semi-crystalline is a small crystal surrounded by non-crystalline materials. These crystals refract light, improve the appearance, and limit the transmission of laser radiation. In turn, they limit the maximum thickness of transmission laser welding. Some plastics can be made of two materials, but this is usually not possible. For example, polyethylene, polypropylene, nylon, polypropylene and polyether ketone, while polystyrene is semi-crystalline, while polystyrene and polystyrene are polystyrene.
Figure 1: Laser transmission welding in polypropylene material shows that the molten zone affects the carbon black filled and unpigmented material very uniformly, with all remaining energy being immediately absorbed by the black material surface (Image courtesy of TWI)
鈻?Interaction of laser types and plastics
The different applications and the interaction of various types of lasers depend greatly on the wavelength produced by the laser, which determines the form in which the plastic absorbs the energy.
The most common form of laser welding is the transmission method, in which the laser beam passes through the top of the part and reaches the surface below the part, where it is heated and melted. The laser wavelengths used are in the range of 750-1500nm and are produced by secondary light, optical fiber, nickel-doped aluminum garnet laser rods (Nd:YAG) lasers. In general, plastics do not absorb this wavelength of radiation as well as ultraviolet or mid-infrared radiation. The level of energy absorption in this range depends greatly on the use of additives in the plastic and whether the plastic is semi-crystalline or amorphous. If the plastic does not contain fillers or pigments, the laser can penetrate into a few millimeters of semi-crystalline plastics, but it is almost not attenuated in amorphous plastics. The absorption level of the laser can be increased by additives such as pigments or fillers, especially carbon black pigments.
Natural uncolored plastics absorb laser radiation to a gradually increasing degree since wavelengths above 1.6渭m, until the absorption of wavelengths above 5渭m in IR is also very strong. In the case of a laser with a wavelength of 2渭m generated by a fiber laser or a hybrid-YAG laser, all plastic materials, whether semi-crystalline or amorphous) are several millimeters above the material. Sheets several millimeters thick can be welded directly without the help of other energy absorbers. This laser is called direct Laser Welding, because the laser beam does not need to pass through the parts above to reach the weld line. Direct laser welding technology has not yet been widely used for plastic joining, but its potential is great.
CO2 laser is a mature material processing tool, commonly used to cut plastic films, sheets and fabrics. The energy of CO2 laser radiation (wavelength 10.6渭m) can be quickly absorbed by the surface of various plastics. Where the laser beam is pointed, the 0.2mm thick plastic is first heated. For thin plastic films, even medium-power lasers (<1000W) are expected to heat quickly and complete the welding quickly. The welding speed can exceed 1000m/min.
鈻?Transmission Laser Welding
In 1985, the transmission Laser Welding technology was first reported, which was carried out on the upper part of an IR-transmissive plastic material and the lower part of a plastic part filled with carbon black. The carbon black absorbs the energy of the laser beam and heats up, forming a weld at the interface of the two parts. On the one hand, since the parts must be black, the parts must be black, but it is still the most commonly used laser welding method. The upper part of the part must receive a portion of the laser energy (usually more than 10%), so that the surface of the lower part will be heated preferentially (Figure 1). The melting depth of the two materials in the picture is basically the same, indicating that the hot spots on the black surface are very concentrated. The black surface acts like a heating element in the part, providing rapid processing of surrounding parts, minimizing heat loss and minimizing deformation or contamination of the joint.
The arrival of alternative energy absorbers for laser welding in 1998 made the color of the joint less obvious. One example is Clearweld, an IR-absorbing pigment that, like other visible pigments, can be applied to the joint by spraying, printing, pads, needles or pens, or added to the underside of the joint (Figure 2). Figure 3 shows a part welded by placing an energy absorber between the joining surfaces of two clear PMMA parts. Almost all color mixes can now be welded by transmission laser welding technology. Fillers with a high plastic content create major problems because the upper part does not allow the laser beam to pass through the joining part. In this case, the filler must be reduced or the particle size must be changed to reduce the scattering of the light or consider an alternative welding process.
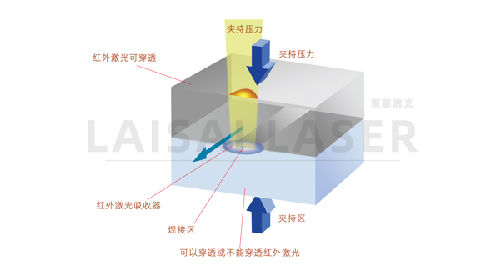
Figure 2: Laser transmission welding on a connector with an IR absorber.
Light TransmissionApplication areas for laser welding include: medical devices, packaging, automotive parts, consumer goods, electronic packaging, textiles.
The application of this technology in textiles is very interesting. The process offers new welding methods for textiles where only the surface is joined, but not the outer surface. In this way, some fibers are not melted and the strength and usually the flexibility of the fabric are not changed. Figure 3: Welding of transparent PMMA containers with IR absorbers. The laser beam is directed underneath the container wall and the weld mark is barely visible.
The process also extends to fiber-reinforced polymer composites, where the composite matrix is heated and melted by the laser source, while the fiber reinforcement remains unchanged during the process.
Transmission laser welding can be used for glass fiber and polymer fiber reinforced composites and matrix materials with low filler content. When using carbon fibers, or when the matrix is black, or when the amount of filler used is high, a direct laser welding method can be used, which does not require the laser beam to pass through the part.
鈻燚irect laser welding
When the laser energy penetrates without the selected radiation wavelength or material type, it melts the plastic surface. The corresponding joining method is called direct laser welding. CO2 lasers were first used for this process. The welding of thin films is expected to reach very high speeds. Examples of various plastic films being welded at speeds of 1200 m/min can be seen. By controlling the power distribution of the laser beam, two plastic films in contact with each other can be cut while leaving a welding area on the cut edge, thereby completing the cutting/sealing during the packaging or bag making process.
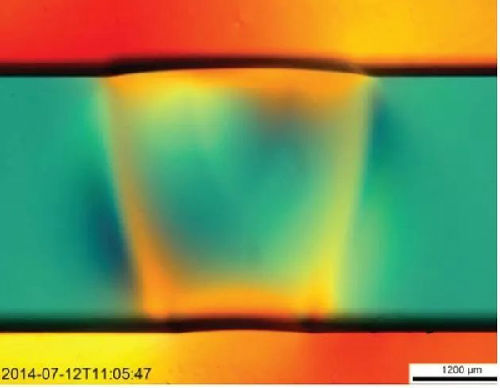
Figure 4: 67W1940nm combined with fiber laser welding at a speed of 4.5m/min, the PMMA melting depth reaches 3mm.
For plastics with a thickness of 0.2-5 mm, conventional welding (Figure 4) and other types of welding (Figure 4) can be connected with a laser source with a wavelength of 2-3渭m. No additional absorber is required, but the transmittance of the plastic must be controlled to ensure stable and consistent welding quality.
鈻燬ummary
Polymer products can be processed using a variety of processing mechanisms (radiation wavelengths are matched to the material) and different types of equipment, such as gantries, robots, scanners or fixed diode arraysLaser Welding. The laser provides efficient energy, precise heating, and local melting. The welding process is fast, strong, and beautiful.
The use of very compact diodes and fiber laser sources can obtain efficient welding processes, which are easy to achieve a high level of automation. This technology is widely used in various industrial fields and product types.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What are the applications of l